 October 5, 2024
October 5, 2024  9 min to read
9 min to read The purpose of this article is to present the most important functionalities and components of the Warehouse Management System (WMS). It will also highlight the advantages of having such a system and its applications.
An essential functionality of WMS is the ability to recognize ongoing business activities in the warehouse, which significantly impacts revenue generation and is critical to the productivity of any company that utilizes warehouses.
The company should be aware of which Warehouse Management System (WMS) software functions have the greatest effect on efficiency.
To implement WMS effectively, various technical aspects need to be considered, such as the scope of daily activities, the level of staff involvement required, inventory lifecycle costs, and supply chain coordination.
Warehouse managers will have to address many strategic questions regarding the scope of WMS software.
This should lead to the implementation of the most suitable solution dedicated to warehouse operations, regardless of industry or integration with a distribution or manufacturing facility. WMS functions are closely linked to the internal processes of any company utilizing a warehouse.
What is a Warehouse Management System?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a specialized platform (software) that optimizes warehouse operations by centralizing and streamlining inventory management and the processes that apply within them.
WMS is designed to handle the day-to-day activities of a warehouse. The WMS system helps coordinate inventory tracking, task allocation for employees, and goods relocation within the warehouse environment.
Modern WMS platforms, often referred to as warehouse management software, encompass a wide range of functions that support key warehouse activities, such as order fulfillment, inventory control, and workforce management.
The tools that make up such a platform are essential for warehouse managers, helping them streamline task execution, improve work accuracy, and quickly respond to operational needs.
Using WMS aims to increase efficiency and productivity, allowing warehouse teams to better meet customer expectations and maintain the company’s competitive position in the market.
By implementing a WMS system, companies gain the flexibility and control needed to adapt to changing market demands and operational requirements.
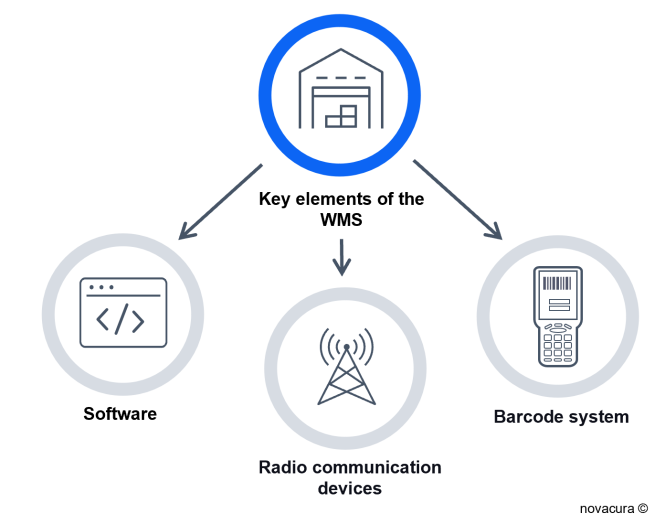
Key elements of the WMS system
The technical aspects of the warehouse management system functions are based on three key elements:
-
Software: This is a digital system that operates on the basis of ERP data exchange, allowing the ERP to be extended with an additional transaction and providing remote control via dedicated applications for mobile and desktop devices.
-
Radio Communication Devices: Mobile devices throughout the warehouse require a wireless network system for communication between servers and the ERP system.
-
Barcode System: The WMS software operates using RFID scanners with a barcode/QR reading function. This is the fundamental element of data collection, and all handling unit operations rely on it to provide continuous data to the system.
Key features of the warehouse management system
In order to properly select a Warehouse Management System, it is necessary to determine the criteria it must meet. Key areas that require digitization should be mapped out. The WMS should have the functions and capabilities to manage these areas.
These include:
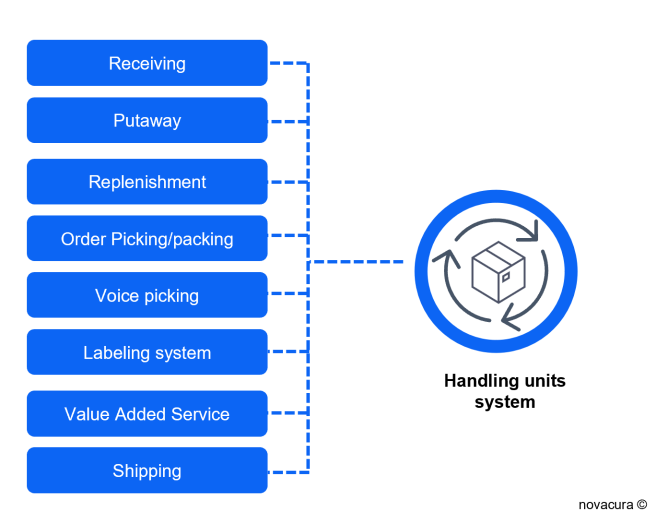
Handling units system
- Receiving: Recording incoming goods in documents using mobile scanners based on the Warehouse Management System (WMS) application.
- Putaway: Assigning incoming goods to inventory throughout the warehouse using WMS-based mobile devices.
- Replenishment: Moving goods from higher racks to lower racks, relocating aging inventory using WMS mobile applications on mobile devices.
- Order Picking/Packing: Picking orders using mobile devices based on WMS applications to plan pick paths and shorten processes.
- Voice Picking: Integrating a voice system with WMS and ERP to allow for hands-free order picking.
- Labeling System: Integrating a printing equipment system with WMS and mobile devices.
- Value Added Service (VAS): Equipping VAS packing lines with handheld scanners and WMS-based desktop applications to track entered material.
- Shipping: Handling outbound shipments with WMS-based mobile applications for accurate shipment processing and fast loading.
Inventory management
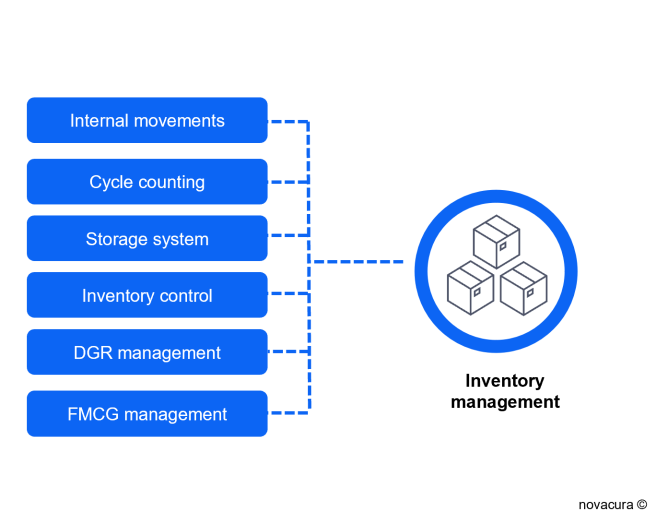
- Internal movements: WMS software provides, via desktop and mobile apps, the ability to control inventory with allocations/relocations and support for inventory aging management, etc.
- Cycle counting: staff can perform periodic inventory counting based on WMS mobile applications installed on mobile devices.
- Storage system: WMS software provides support for a pallet storage system, rack labeling system, and merchandise classification, which allows immediate allocation of goods to required areas.
- Inventory control: inventory controllers are supported by WMS-based mobile applications to immediately resolve inventory discrepancies.
- Hazardous goods management: users can be alerted by the WMS that they are dealing with DGR goods because they require proper storage, often in refrigerators or isolated high-security areas.
- Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG): the WMS can manage temperature-sensitive goods and those with special storage requirements.
Personnel management
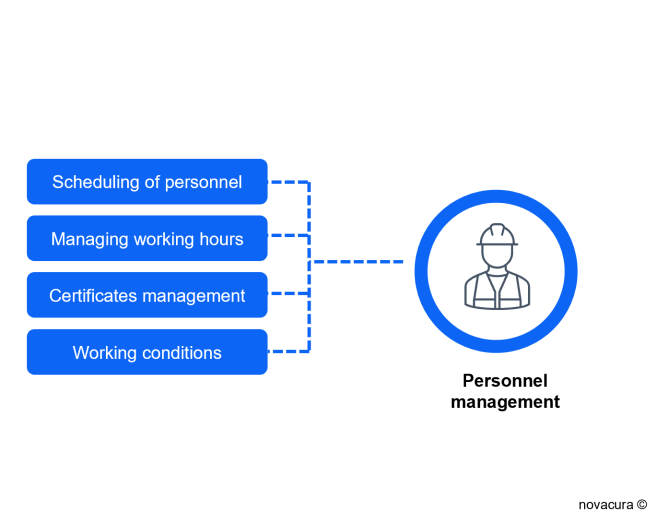
- Scheduling of Personnel Shifts: The Warehouse Management System (WMS) allows for the scheduling of shifts, assessing the required equipment needed to perform specific tasks.
- Managing Working Hours: Managers and supervisors, using WMS-based software, can track the exact hours assigned to perform specific tasks in the warehouse.
- Certificates Management: The WMS software enables the tracking of periodically updated licenses and personnel certifications for warehouse equipment such as lift trucks, forklifts, combi trucks, etc.
- Management of Working Conditions: WMS software can provide a system for recognizing the working conditions in specific warehouse areas and notifying personnel of any hazards or requirements.
Returns management
- Return Packaging Management: The WMS software supports a labeling system and allows tracking the packing cycle of return packaging, excluding damaged boxes from the process, etc.
- Return Merchandise System (RMA System): The WMS handles returned goods that require quality assessment before entering the warehouse. The WMS should allow the implementation of additional quality control transactions beyond those available from the ERP.
Reports and analytics
- KPI Management: The Warehouse Management System (WMS) allows all data to be pulled from all departments, providing a transparent and adjustable overview that helps managers control overall processes.
- Reporting: Using the built-in functions of the WMS, managers and office administrators can create weekly reports to track current processes.
- Forecasting: Based on the WMS software, staff can create reports to predict certain events in the warehouse and avoid process disruptions.
Supply Chain management
- Shipping System: WMS allows tracking shipments from the door to the warehouse and vice versa based on the Proof of Delivery (POD) function.
- Communication with Carriers through the EDI System: WMS software enables connectivity with third-party carriers’ Transportation Management Systems (TMS), facilitating the update of shipment data, and more.
Financial management
- Invoicing system: based on the WMS system, all departments can collect all financial data. External third parties can send invoices to the internal systems.
Deep ERP integration
- Connecting Existing Systems: WMS software can integrate all systems across the organization, pulling required data from all departments (such as the Transportation Management System (TMS), reporting and financial systems, operational processes, etc.).
- ERP Integrations: WMS software should be linked to the ERP system as an additional layer to increase the number of transactions, providing personnel throughout the organization with direct insight into current operations.
Autonomy, flexibility, and operating training program
- Easy interface: WMS mobile applications can provide ease of use and reduce training time by simplifying the user interface on a mobile device for the operations staff member.
- Autonomous warehouse: WMS software allows internal staff to build their own system applications without external support.
- Flexibility: WMS software can provide BPM-based functionality that allow add new system transactions and maintain the on-fly operational changes.
Benefits from WMS
Novacura offers Warehouse Management System (WMS) and solutions built on top of an ERP system. Novacura Flow is a software that enables the creation of customized business processes (BPM) and mobile and desktop applications. These applications can exchange data with the ERP system in real-time. Novacura Flow provides WMS functionality covering essential warehouse management functions and department operations.
The example presented above explains how users can use Novacura Flow, with access to Novacura Flow Studio, environment for developing applications for internal operational needs in warehouses.
Here are the main benefits of a WMS built on Novacura Flow software:
Novacura Flow offers several advantages for warehouse management:
- Reduced Costs: Novacura Flow enables the development of operational applications without extensive and costly third-party software support.
- Zero Information Errors: Eliminate information errors and increase inventory accuracy.
- Reduced Information Acquisition Time: Reduce the time and effort required to collect and process inventory and customer order data.
- Increased Warehouse Capacity: Increase warehouse capacity by allowing products to flow through the warehouse faster.
- Optimized Space Utilization: Update information for warehouse workers on where to put products in each location based on known dimensions, optimizing space utilization.
- Increased Labor Productivity: Boost labor productivity by directing warehouse workers’ tasks and scheduling work time accordingly.
- Minimized Warehouse Losses: Reduce inventory discrepancies and gain better control over warehouse demand, minimizing losses.
- Integration with ERP: Novacura Flow facilitates the integration of all internal systems with ERP based on APIs and IoT connectors for machines to retrieve more operational data from the shop floor once the warehouse is connected to the manufacturing plant.
Summary
Novacura Flow encompasses significant features for Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), as recognized by Gartner. Gartner acknowledges the importance of specific features in WMS systems, and Novacura Flow-based WMS capabilities align with Gartner’s Magic Quadrant concept. This concept is an analytical technique that categorizes the best-fit WMS software for business requirements.
Customer case
Learn more about WMS implementation from Novacura in an US food industry, at Land O'Frost company.

Novacura has been a steadfast support for businesses across various industries for almost 20 years. Our commitment is to assist customers in streamlining processes and enhancing operability with Warehouse Management System (WMS) features in their warehouses. Our solution is designed to provide a significant return on investment (ROI), particularly in terms of reducing reliance on third-party programming support and optimizing labor hours for operational processes. Contact us today and discover how we can contribute to the success of your company.











