Job Safety Analysis: what it is & how to make it better
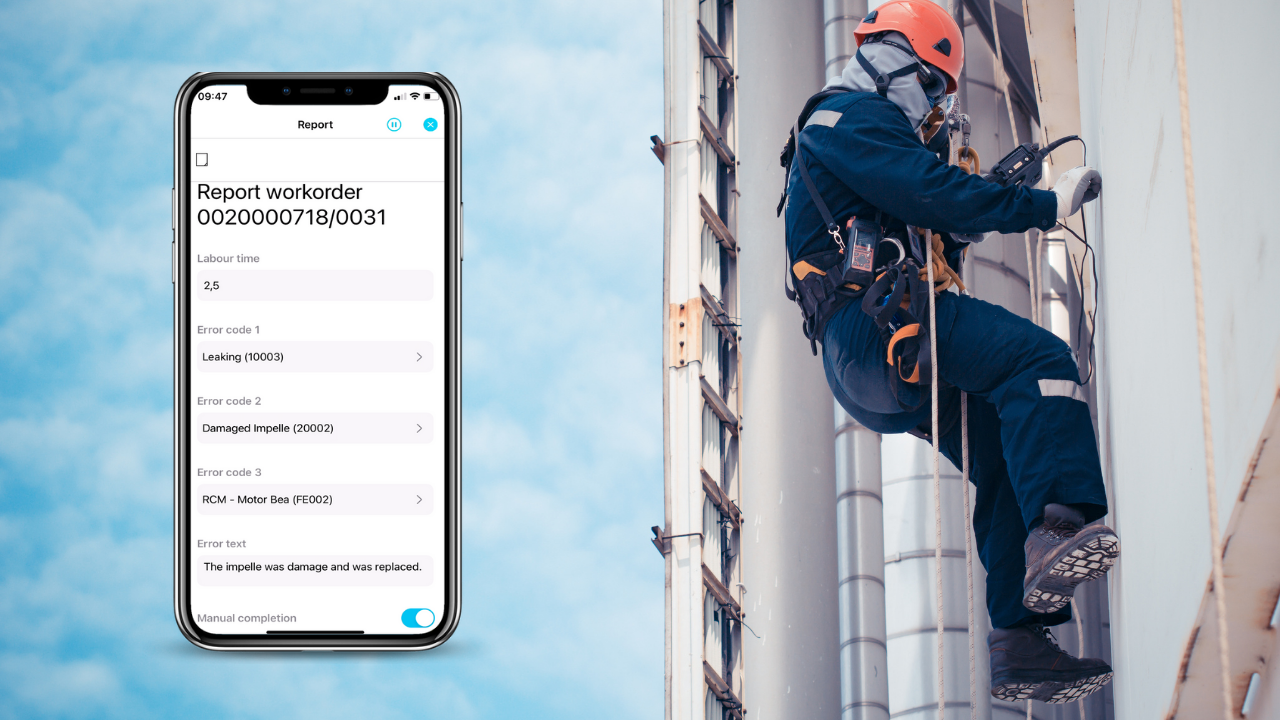
What is a Job Safety Analysis (JSA)? Safety is always a concern on the job site. Safety hazards can put workers in danger, cause serious illness or injury and potentially lead to devastating lawsuits. That’s why many businesses use the Job Safety Analysis (JSA) to help mitigate health and safety risks on work sites. But completing a JSA every day, for every job site, requires a lot of time and effort. It can be easy for workers to half-heartedly complete their JSAs, or ignore them altogether—which can lead to serious consequences. So today, we want to discuss the JSA process, and how you can make it easier using Novacura Flow. Why is it important to conduct a job safety analysis? A job safety analysis (JSA) is a critical first step in promoting workplace safety. By breaking down specific tasks to pinpoint potential hazards, a JSA helps reduce the chances of accidents and injuries, keeping workers safer on the job. In fields like construction, conducting a JSA before each shift and prior to starting work offers a proactive approach to identifying risks that might otherwise go unnoticed. Recognizing hazards early on provides an opportunity to address them, whether through elimination, substitution, or mitigation strategies, reducing the likelihood of incidents. Prevention is key—every accident avoided is a direct result of proactive safety measures and a commitment to zero-injury principles. A well-conducted JSA exemplifies this commitment, reinforcing that safety is not only a priority but a continuous process. For employers, job safety analysis brings additional benefits beyond worker protection. A thorough JSA can improve job site efficiency by reducing delays associated with unaddressed hazards and compliance issues. Identifying risks in advance allows employers to manage resources more effectively and ensure regulatory compliance, ultimately saving time and reducing operational costs. Though a JSA is just one part of a broader workplace safety program, its impact on reducing accidents and fostering a safe, compliant environment can be significant. How many JSAs should a company conduct? Ideally, you would conduct a JSA for every business process—but that takes a lot of time and effort. Focus your efforts on the processes: where previous injuries have occurred that are high-risk tasks You will need to update the JSA whenever conditions change. This can mean changes to equipment, location, or even weather: if the business process changes in any way, you need to review/update the JSA too. You should also review and update the JSA whenever injuries occur on the job. Best practice is to review, and update as required, prior to beginning the task. How to create a JSA Map the process Maybe you’ve already done this. If so, awesome! You’ve already built the foundation of a successful JSA. If not, you’ll want to start by breaking the process down into tasks. For example, if you were to create a JSA for drinking your morning cup of coffee, you might start with something like this: Task Hazard Recommendations Pour coffee in cup Add sugar to coffee in cup Drink coffee Identify the safety hazards associated with each step of the process For […]
learn more
How to improve material traceability in manufacturing
Inventory control over a long period of time can no longer rely on manual data entry using paper forms. The dependence on the manual data entry method cannot be verified in a short period of time and can cause inventory discrepancies that have serious financial implications for the organization. Traceability of goods in manufacturing requires digital inventory management software. Production clerks equipped in mobile devices with embedded software can take control of the entire inventory management process. Handheld computers and mobile scanners operating with barcodes, QR codes, RFID technology are able to ensure proper supervision of the internal flow of materials. Providing barcode material labels when products are inbounded is the solution that should be implemented in any factory. There is no doubt that the use of mobile devices with embedded operate software in manufacturing can influence all stages of production and increase its quality of: Material consumption – consumption registering and preventing shortage ofraw materials. Processing inbound – good traceability from dock registration to inventoryputaway process. Order picking – accurate collection from direct stock locations. Packing and pelletizing – easy determining delivery destination and good quality order checks. Outbound and shipping management – efficient dispatch and reliable ETA with track & trace. Inventory control – quick inventory control and accurate cycle count. What is manufacturing traceability? Manufacturing traceability refers to the ability to monitor and track materials, parts, and products—whether individually, by batch, lot, or shipment—throughout the entire manufacturing process and into the supply chain. This capability has evolved significantly from the days of manual records and paper-based tracking. The introduction of barcode technology was transformative, enabling manufacturers to track any item associated with a barcode, including raw materials, components, subcomponents, and finished goods. Modern manufacturing traceability systems go further by leveraging advanced tools like barcodes, RFID, and data analytics to provide real-time visibility into production processes, not just physical items. This comprehensive traceability begins the moment raw materials and parts enter production and continues until the final product exits the facility. By offering detailed insights into each stage of production, today’s systems help manufacturers ensure quality, boost efficiency, and maintain regulatory compliance, ultimately enhancing operational control and customer satisfaction. Manufacturing in the COVID-19 era – Top 3 challenges and how to overcome them (PDF) Top 3 challenges for manufacturers during the pandemic What are the root causes of the challenges? Proposed solution How to implement iT Download Effective traceability of materials Embedded software connected to ERP systems can be enough to fulfil general needs of particular warehouse management but its customization is almost impossible. Modification of ERP system is difficult and time consuming therefore any sort of random software cannot be suitable for complexity of production process. The manufacturing industry is closely dependent on the dynamic changesoccurring in each industry sector. Ongoing changes regarding market demand are forcing factories to respond. Adjusting production lines and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) is already part of its strategy. To secure effective material traceability, manufacturing facilities should consider selecting the most appropriate solution with the possibility of flexible software modification. The software should not only be suitable for the existing hardware, […]
learn more
Shop Floor Data Collection Software: How to integrate equipment with business systems
To manage means to measure. And your management decisions are as good as the quality of data you used to base them on. Management decisions are made based on “business systems” (Reporting systems – business intelligence, ERP systems, Planning systems APS, MES systems). But these systems have problems with acquiring appropriate information from original information sources. Integrating the systems would be a solution to this, but it’s challenging due to two problems: On the Shop floor side – different devices have different protocols, some are new and some can be over ten years old. There are various business systems on the IT Systems side (APS, MES, ERP, MRP, WMS, QMS). They all use different protocols, provide other information and have independent databases (usually not synchronized). What Is Shop Floor Control Software? Shop Floor Control (SFC) software typically – but not always – part of a Manufacturing Execution System (MES), is a tool that captures, compiles, and analyzes the data needed to make your manufacturing tractable. This set of software constantly gathers data on human input as well as automated systems to inform what is happening right on the shop floor as work is in progress. With shop floor management software, you gain the ability to monitor every detail of factory activity in real time. Detailed reports can reveal essential metrics such as machine runtime, material usage, work remaining, and overall production efficiency. These insights empower managers to make timely, informed decisions that can improve productivity and reduce downtime. Moreover, SFC software can provide a broad perspective that spans multiple departments, individual machines, or even various manufacturing sites. This capability allows for the tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) from numerous data sources, offering a comprehensive view of the factors driving your company’s production performance. By leveraging SFC software, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and better understand the variables influencing their overall output, helping to optimize operations and support continuous improvement across facilities. Solution The low-code BPM platform, Novacura Flow can integrate with all devices on the shop floor side as well as all systems on the IT side. This makes it an ideal solution for bridging the gap between equipment and business systems. Protocols that Novacura Flow support – by devices side How we can communicate with different products: Via a rest-based IoT-Hub, as Azure IoT Via a OPC-UA server Via a machines PLC over ModBus Directly with a machine over TCP/IP Directly from the Novacura Flow-app with a device over BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) What type of equipment can we connect? Production Robots — automatically read all information, detect downtime, track the number of cycles, and identify alerts. Vision AI cameras — to identify mistakes, take action and record the “incident” for quality purposes Semi-automated Machines used for production — like CNC, 3D Printers – as above, to read information about performance progress, number of prepared components, downtime, alert detection Different gauges/measurers — measure various parameters on the shop floor, such as dust, humidity, temperature, noise, vibrations, and power consumption (including voltage and amperage). Internal access control system — to monitor if a worker leaves or enters the warehouse, track their availability, and […]
learn more
Field Service Management Software connected to ERP
Today, companies that operate in field services and provide maintenance are often closely dependent on ERP systems. However, ERP capabilities often go far beyond the scope of FSM processes, which can only be supported by highly customized software tailored to the specific needs of service industry businesses. The system transactions in ERP allow the organization to run basic operations but does not include the detailed data needed to perform all operations dedicated to FSM effectively. For this reason, field personnel still perform FSM-related tasks with typical paperwork in their hands and then record manually in the ERP system. Manual data entry causes many discrepancies in the system and delays, which lead to much more serious problems and can have significant financial consequences. In addition, inefficiencies in FSM lead to problems with data flow, which is very important for industries that provide services such as public transport, logistics, energy supply, railway installations maintenance, machinery maintenance in manufacturing, and many others. Only a company with mobile solutions for industrial maintenance in the hands of its personnel will be effective enough to deal with the day-to-day business problems associated with field services and maintenance in a highly dynamic environment. What is field service management software? Enterprise Field Service Management software is a system that provides personnel with the capabilities to perform field services and maintenance. Organizations that depend on industrial installations in different locations around big cities and the entire country must often provide services to these installations to ensure their continued functionality. Therefore, the FSM software capabilities should deliver these functions: Mobile access: the FSM should provide mobile applications that can be used by field personnel on mobile devices where they can perform checklists, record damages, system functionality faults, and all operations that are needed for their industry-specific equipment and installation requirements. Offline mode: organizations that are location-dependent with limited network access should be able to record data on mobile devices that can be updated in the ERP system when the network is available again. The Novacura apps have an offline mode. Field workers can retrieve information about the equipment needed for the inspection or reparations and then update the data in the central system. System customization: each industry requires a different approach to field service and maintenance, and business requirements can change; therefore, FSM should be easy to adapt when needs increase or system transaction models change. Real-time data sharing: the FSM is dependent on remote field staff, but the decision-making process should be centralized; therefore, it is important that the FSM continuously provides real-time data to the central management unit to allocate existing resources better. Work order management: the FSM should provide functions accessible from mobile devices that allow easy material pre-order, tool/equipment allocation, process step updates, and even direct access to work instructions with remote assistance. Personnel management and scheduling: the FSM should have built-in functionality for allocating various resources and scheduling personnel, which is critical for any field service to provide services in a timely manner and schedule sufficient working hours, as well […]
learn more
Field service management software that connects to IFS: key benefits
Service and maintenance projects necessitate focused attention on FSM-based control systems. The intricacies of service work highlight that FSM can optimize efficiency only when underpinned by customizable software that aligns with business requirements. When determining a cost-effective approach to procuring FSM software, companies should assess its integration capabilities with ERP systems. This approach enables businesses to maintain lower costs when expanding the ERP system with supplementary FSM functionalities. Utilizing the right FSM software facilitates the customization of functionalities without the need for external software development support. Consequently, this approach ensures ERP modifications remain cost-free, effectively establishing the FSM software as an independent layer integrated atop the ERP. Some ERP providers, such as IFS, offer specialized integration capabilities that connect the ERP system with FSM software. This integration empowers IFS users to manage field service and maintenance functions within a segregated system environment. This enables IFS users to align maintenance standards with business objectives, with a strong focus on cost efficiency. Linking FSM software to an IFS ERP system enhances a company’s technological capabilities, delivering numerous benefits, including free customizations and more (as detailed below). What is field service management software? Many industrial companies are required to adhere to particular standards related to health, reliability, customer satisfaction, safety, quality, and even security. Field service management software plays a crucial role in upholding and preserving these standards, facilitating the use of digital systems to collect data and carry out essential tasks. FSM software facilitates the integration of data from ongoing operations into all maintenance practices and methods. This empowers maintenance departments to oversee their work, enhance the efficiency of maintenance tasks, address customer concerns, and respond to emergency situations effectively. Internal: An in-house maintenance structure that relies on internal resources and operates independently, managing facilities and remote installations using only the company’s own personnel. External: Involves external organizations that provide the required assistance independently, often utilizing third-party services to maintain the operational efficiency of equipment and installations. What is a field service platform? FSM software comprises two primary components that collectively play a crucial role in overseeing operations at remote locations. Together, they constitute an integral field service platform. These essential components for effective field service and maintenance management include: Mobility: FSM software should offer mobile functionality for field workers who utilize customized mobile applications on their mobile devices. This empowers them to conduct equipment and installation inspections with enhanced speed and accuracy, ultimately improving the efficiency of maintenance operations. Portals: FSM software should facilitate comprehensive control over field operations through a centralized administrative hub. Here, managers and shift planners can meticulously plan maintenance schedules, make informed forecasts, and devise maintenance strategies based on pertinent operational needs, all within a single interactive portal. This consolidated view allows for a more streamlined approach to maintenance management. Indeed, only a select few systems in the market offer a complete maintenance platform that aligns with the comprehensive criteria needed for FSM software. Novacura presents the Novacura Flow software solution, which functions as a service platform, delivering users with the full spectrum of FSM capabilities along with a platform […]
learn more
How to choose mobile field service management software?
Field service and maintenance management software should provide on-site management and technical services for businesses in a variety of industries, including manufacturing facilities, commercial and government buildings, hospitals, railroad infrastructure, and even large sports complexes, which require extensive security compliance control to guarantee thousands of visitors complete safety during sporting events. Field services and maintenance should include a strategic planning function, which is very difficult to accomplish without proper instruments for extensive management of operations at various locations across the country. Companies such as SweMaint and Holmen, whose successful operations are closely dependent on well-managed field and maintenance services, are just one example. These companies operate in manufacturing, maintenance, and field service, providing flexible and consistent support for locations and equipment. Despite the different areas of field service and maintenance operations, these companies require cost-saving results when performing maintenance services, as well as more efficient labor management. Obviously, these companies wanted to make the right choice on FSM software to avoid poor planning and organization that lead to poor maintenance management and backlogs. Buying FSM software can be pretty difficult if the software does not offer specific capabilities and features, giving companies visible benefits in the long run. What are the features of field service software? FSM software provides control over critical elements in industrial operations. Therefore, in practical maintenance, it is important to provide its users with software that includes certain functions and allows users to develop a maintenance management framework with remote control of industrial equipment and installations. Here are several important features of FSM software: Work order management – FSM should perform as a job scheduling software where all job progress is visible in the system and can be easily tracked and controlled by planners providing the organization with real-time visibility software functions. Constant data collection – information acquisition and constant data exchange require FSM to process as analytical data software, where staff can get analytical information at any time to prepare better forecasts. Personnel Management – to perform all operations most efficiently, FSM should support working hour assignments and act simply as workforce management software, making scheduling easier even in unpredictable cases like personnel shortages. Business Process Management – high workloads in various industries require simplifying the most complex operations in an organization, so FSM should provide business automation software capabilities where processes can be simplified with a better user interface, etc. Deep ERP integration – FSM software can maintain higher performance when it has integration software capabilities, allowing it to connect existing systems in the organization and integrate with another ERP system and implement that way the ERP evergreen strategy. Who are the key players in field service management? The features above are absolute standards for the successful procurement of maintenance software. Companies that want to invest in process optimization should also consider performance metrics that allow them to collect relevant data from the entire operation, which can include maintenance performance metrics or financial data with an assessment of annual maintenance expenses and much more. Key players who provide FSM software […]
learn more